
Absolute logarithmic units can be converted into non-logarithmic units of the same physical values. Absolute units are ideal for describing a single value, not a ratio of two values.

There are absolute and relative units.Ībsolute logarithmic units express a physical value referenced to some specific value, for example, dBm is an absolute logarithmic unit of power with reference to 1 mW. Logarithmic units are widely used in science, technology and even in everyday things like photography and music. Log 5(25) = 2 Classification of Logarithmic Units In more simple words, a logarithm is an answer to the question: “How many times do we have to multiply one number to get another number?” For example, how many times do we multiply 5 to get 25? The answer is 2 or In other words, the logarithm is a quantity representing the power to which a fixed number called the base must be raised to produce a given number. The logarithm is the inverse operation to exponentiation. Some people even think that logarithmic values more related to the era of slide rules than to the modern digital world. Looks convenient? Yes, but not to everyone! Actually, all people who are not mathematically or technically inclined can be easily confused when dealing with quantities expressed in logarithmic units like decibels. At the same time, the sound power of quiet conversation is 0.000000001 W or 30 dB SWL. For example, the sound power of a Saturn V rocket is 100,000,000 W or 200 dB SWL (dB referenced to the sound power level 10⁻¹² W, it is described below). Logarithmic units allow representing a very large range of ratios by a small convenient number similar to scientific notation. The sound power of a Saturn V rocket is 100,000,000 W or 200 dB SWLĪ logarithmic scale is often used when there is a large range of quantities like sound pressure, earthquake strength, light intensity, various frequency-dependent values like musical intervals, in antenna engineering, electronics, acoustics, RF engineering.
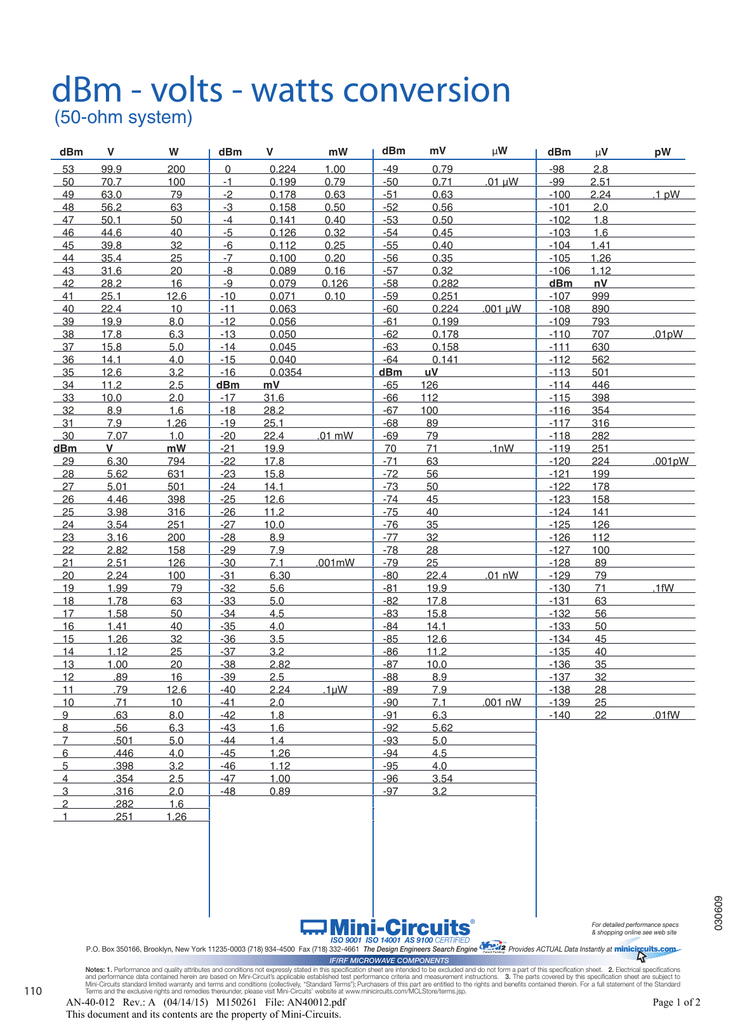
Return to Basic Electronics Concepts menu. Voltage Current Power Resistance Capacitance Inductance Transformers Decibel, dB Kirchoff's Laws Q, quality factor RF noise Waveforms More Basic Electronics Concepts & Tutorials: Converting from dBm and from the other values of dBW and watts to voltage, both peak to peak and RMS can be useful in many areas of RF design. These tables of dBm, dBW, watts and miliwatts to volts are useful to discover the voltages present. It is applicable to many high power applications. It is applicable to many medium power applications. This conversion table charts the values for dBm against milliwatts and the relevant voltage expressed in volts. dBmĭBm - milliwatts - Volts conversion table:. It is applicable to many lower power applications. This conversion table charts the values for dBm against milliwatts and the relevant voltage expressed in millivolts. dBm / millivolts / milliWatts conversion table Also as the milliwatts change to watts, the change in the table is made. These have been chosen because the voltages move from readings measured in millivolts to those in volts. The table below provides a chart to convert between dBm, watts and voltage - peak to peak in a 50Ω system.Īlthough voltage levels are unlikely to rise to significant levels which might cause damage for power levels measured in dBm, the voltages are often used in other calculations. When working with RF power, it is often useful to know the voltage level for a given power. DBm Milliwatts, Watts & Voltage Conversion Chart Conversion table to convert between dBm, Watts and voltage in a 50 Ω system.ĭecibels, dB - the basics Decibels levels table dBm to dBW & power conversion chart dBm to watts and volts conversion chart dB, decibel online calculator Nepers


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
